Much has been written about the bicycle’s role as a vehicle of women’s liberation. But far less is known about another critical technology women used to forge new mobile and public lives – cyclewear. I have been studying what Victorian women wore when they started cycling. Researching how early cyclists made their bodies mobile through clothing reveals much about the social and physical barriers they were navigating and brings to light fascinating tales of ingenious inventions.
Cycling was incredibly popular for middle- and upper-class women and men in the late 19th century, and women had to deal with distinct social and sartorial challenges. Cycling exaggerated the irrationality of women’s conventional fashions more than any other physical activity. Heavy, layered petticoats and long skirts caught in spokes and around pedals. Newspapers regularly published gruesome accounts of women dying or becoming disfigured in cycling crashes due to their clothing.
Fortunately, little was going to stop women riding and they rose to these challenges in a plethora of ways. Some took to wearing “rational” dress, such as replacing skirts with bloomers. While this was safer and more comfortable for cycling, dress reform was controversial. It was not unusual for onlookers who felt threatened by the sight of progressive “New Women” to hurl insults, sticks and stones. Other women adopted site-specific strategies to minimise harassment, such as cycling in conventional fashions in town and changing into more radical garments for “proper riding”.
Some pioneering women came up with even more inventive strategies. Remarkably, some Victorians not only imagined, designed, made and wore radical new forms of cyclewear but also patented their inventions. The mid-1890s marked a boom in cycling and also in patenting, and not only for men. Cycling’s “dress problem” was so mobilising for women that cyclewear inventions became a primary vehicle for women’s entry into the world of patenting.
The patents for convertible cyclewear are particularly striking. These garments aimed ambitiously for respectability and practicality. Inventors concealed converting technologies inside skirts, including pulley-systems, gathering cords, button and loop mechanisms and more, that enabled wearers to switch between modal identities when required.
Alice Bygrave, a dressmaker from Brixton, lodged a UK patent in 1895 for “Improvements in Ladies’ Cycling Skirts”. She aimed to “provide a skirt proper for wear when either on or off the machine”. Her parents owned a watch- and clock-making shop in Chelsea and her brother and sister-in-law were professional cyclists. Her invention brings all of these influences together in an ingenious skirt with a dual pulley system sewn in the front and rear seams that adjusts height according to the needs of the wearer. Bygrave also patented her invention in Canada, Switzerland and America, and it was manufactured and distributed by Jaeger. It was a hit, and was sold throughout the UK and America. It even made its way to Australia.

Julia Gill, a court dressmaker from north London, registered her convertible cycling skirt in 1895. Her aim was to “provide a suitable combination costume for lady cyclists, so that they have a safe riding garment combined with an ordinary walking costume”. This deceptively ordinary A-line skirt gathers up to the waist via a series of concealed rings and cord into what Gill called a “semi-skirt”. The lower flounce, when made from similar material to the jacket, creates a stylish double peplum. The inventor also recommended combining the skirt with some rather splendid “fluted or vertical frilled trowsers”.
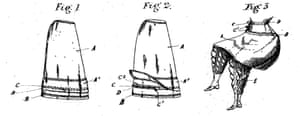
Mary and Sarah Pease, sisters from Yorkshire, submitted their patent for an “Improved Skirt, available also as a Cape for Lady Cyclists” in 1896. As the name suggests, this is two garments in one – a full cycling skirt and a cape. The wide waistband doubles as a fashionable high ruché collar. This garment is one of the more radical designs of the period because the skirt completely comes away from the body. Cyclists wanting to ride in bloomers could wear it as a cape or use the gathering ribbon to secure it to handlebars, safe in the knowledge they could swiftly replace the skirt should the need arise.
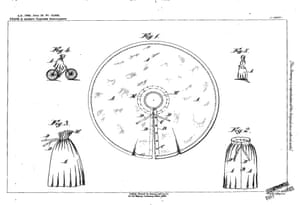
Henrietta Müller, a women’s right’s activist from Maidenhead, registered her convertible cycling patent in 1896. Unusually, the inventor addressed an entire three-piece suit – a tailored jacket, an A-line skirt that can be raised in height via loops sewn into the hem that catch at buttons at the waistband, and an all-in-one undergarment combining a blouse and bloomer. Müller was committed to the idea of progress for women, and not content with trying to fix one element when she could see problems with the entire system. She was acutely aware of the politics and practicalities of pockets for newly independent mobile women. As a result, this cycling suit features five pockets, and Müller encouraged users to add more.
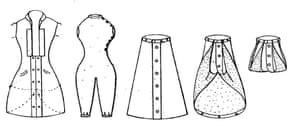
These inventions are just some of the fascinating ways early female cyclists responded to challenges to their freedom of movement. Through new radical garments and their differently clad bodies they pushed against established forms of gendered citizenship and the stigma of urban harassment. Claiming their designs through patenting was not only a practical way of sharing and distributing ideas; it was also a political act.
These stories add much-needed layers and textures to cycling histories because they depict women as critically engaged creative citizens actively driving social and technical change. Importantly, they remind us that not all inventions are told through loud or heroic narratives. These inventors put in an awful lot of work to not be seen. They were successful in many ways, yet the nature of their deliberately concealed designs combined with gender norms of the time means they have been hidden in history – we have yet to find any examples in museums.
As such, they raise questions: what else don’t we know about? How can we look for other inventions hidden in plain sight? And if we learn more about a wider range of contributors to cycling’s past, might it change how we think about and inhabit the present?
• Dr Kat Jungnickel is a senior lecturer in sociology at Goldsmiths, University of London. More about her research, including re-creations of convertible costumes and free sewing patterns inspired by the patents, is available at her website and in Bikes & Bloomers: Victorian Women Inventors and their Extraordinary Cycle Wear, out now through Goldsmiths Press. Patent illustrations accessed in the European Patent Office Espacenet Database.


View all comments >